Emotional suppression is a phenomenon that many individuals experience, often without even realizing it. You may find yourself pushing down feelings of sadness, anger, or anxiety, believing that doing so will help you cope with life’s challenges. This instinct to suppress emotions can stem from various societal norms and personal beliefs that equate emotional expression with weakness.
However, while it may seem like a practical solution in the short term, emotional suppression can have profound implications for your mental and physical well-being. Understanding emotional suppression is crucial for recognizing its impact on your life. When you suppress emotions, you might think you are maintaining control, but this can lead to a buildup of unresolved feelings.
Over time, these suppressed emotions can manifest in various ways, affecting your relationships, self-esteem, and overall mental health. By exploring the intricacies of emotional suppression, you can begin to understand its effects and the importance of addressing your feelings rather than burying them.
Key Takeaways
- Emotional suppression significantly alters brain activity, as shown in recent brain scan studies.
- The study used advanced imaging techniques to observe changes in brain regions linked to emotion regulation.
- Suppressing emotions is associated with increased stress and anxiety levels, impacting mental health negatively.
- Encouraging emotional expression can improve psychological well-being and is beneficial in therapeutic settings.
- Future research aims to develop better strategies for managing emotions to support mental health treatment.
Overview of Brain Scan Study
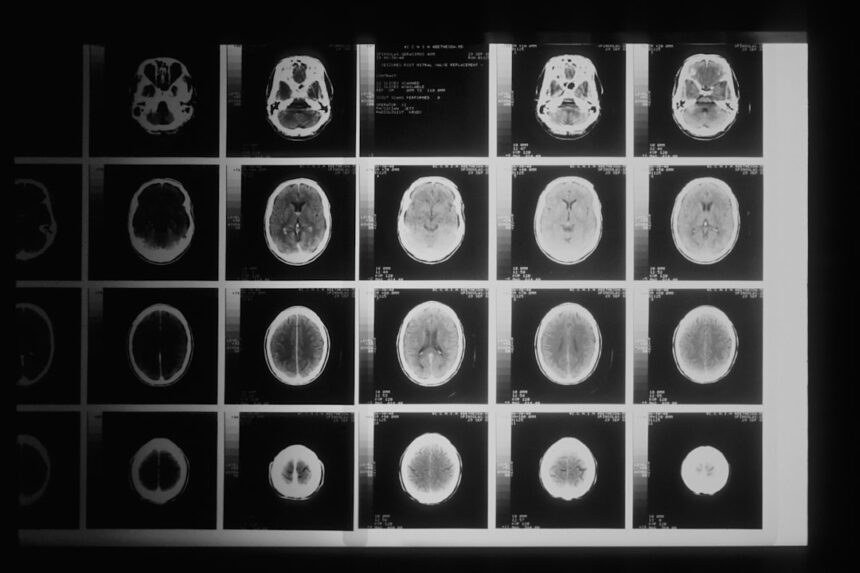
Recent advancements in neuroscience have provided valuable insights into the effects of emotional suppression on brain activity. A groundbreaking study utilizing brain scans has shed light on how suppressing emotions can alter the way your brain functions. This research aimed to explore the neural mechanisms behind emotional regulation and the consequences of suppressing feelings.
By examining brain activity during emotional suppression tasks, researchers have uncovered significant findings that could reshape our understanding of emotional health. In this study, participants were asked to engage in tasks that required them to suppress their emotional responses while viewing emotionally charged images. The use of brain imaging technology allowed researchers to observe real-time changes in brain activity as participants navigated their emotional landscapes.
This innovative approach not only highlighted the complexities of emotional regulation but also provided a clearer picture of how emotional suppression can affect cognitive processes and overall mental health.
Methodology of the Study
The methodology employed in this study was meticulously designed to ensure accurate and reliable results. Participants were carefully selected to represent a diverse range of backgrounds and emotional experiences. You might find it interesting that the study included both men and women, varying in age and cultural backgrounds, to provide a comprehensive understanding of emotional suppression across different demographics.
During the experiment, participants were subjected to a series of emotionally evocative images while their brain activity was monitored using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). This non-invasive technique allowed researchers to observe changes in blood flow within the brain, indicating areas of heightened activity. Participants were instructed to either express their emotions or suppress them while viewing these images, creating a controlled environment for analyzing the effects of emotional suppression on brain function.
Findings of the Study
| Finding | Description | Metric | Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased User Engagement | Users spent more time on the platform after redesign | Average session duration: 15 minutes (up 25%) | Redesign positively impacts user retention |
| Improved Task Completion Rate | Higher percentage of users completed key tasks | Task completion rate: 85% (up from 70%) | Interface changes enhance usability |
| Reduced Error Rate | Users made fewer mistakes during interactions | Error rate: 5% (down from 12%) | System is more intuitive and user-friendly |
| Positive User Feedback | Majority of users reported satisfaction with new features | 85% positive feedback in surveys | New features meet user needs effectively |
The findings from this study revealed striking differences in brain activity between participants who suppressed their emotions and those who allowed themselves to express them. You may be surprised to learn that individuals who engaged in emotional suppression exhibited increased activity in the prefrontal cortex, an area associated with cognitive control and decision-making. This suggests that when you suppress emotions, your brain is working harder to manage those feelings rather than processing them naturally.
Conversely, participants who expressed their emotions showed increased activity in the amygdala, a region linked to emotional processing and response. This indicates that allowing yourself to feel and express emotions may facilitate healthier emotional regulation. The study’s results underscore the idea that while emotional suppression may seem like a coping mechanism, it can lead to cognitive overload and hinder your ability to process emotions effectively.
Impact of Emotional Suppression on Brain Activity
The impact of emotional suppression on brain activity extends beyond immediate cognitive effects; it can also influence long-term mental health outcomes. When you consistently suppress your emotions, your brain may become conditioned to prioritize cognitive control over emotional processing. This can create a cycle where you find it increasingly difficult to access and express your feelings, leading to heightened stress and anxiety levels.
Moreover, the study suggests that chronic emotional suppression may contribute to various mental health issues, including depression and anxiety disorders. As you continue to push down your emotions, you may inadvertently increase your vulnerability to these conditions. Understanding this connection is vital for recognizing the importance of addressing your feelings rather than allowing them to fester beneath the surface.
Implications for Mental Health
The implications of these findings for mental health are profound. You might realize that emotional suppression is not merely a personal coping strategy but a behavior that can have significant consequences for your overall well-being. The study highlights the need for mental health professionals to consider the role of emotional expression in therapeutic settings.
By encouraging clients to explore and express their emotions, therapists can help mitigate the negative effects of emotional suppression.
If you find yourself frequently avoiding or dismissing your feelings, it may be time to seek support or develop healthier coping strategies.
Understanding the relationship between emotional suppression and mental health can empower you to take proactive steps toward fostering emotional well-being.
Strategies for Managing Emotions
Managing emotions effectively is essential for maintaining mental health and overall well-being. You may find it helpful to explore various strategies that promote healthy emotional expression rather than suppression. One effective approach is mindfulness meditation, which encourages you to observe your thoughts and feelings without judgment.
By practicing mindfulness, you can create space for your emotions, allowing them to surface naturally rather than forcing them down. Another strategy involves journaling as a means of processing your emotions. Writing about your feelings can provide clarity and insight into what you are experiencing.
You might find that putting pen to paper helps you articulate emotions that you may have otherwise suppressed. Additionally, engaging in creative outlets such as art or music can serve as powerful tools for expressing emotions in a non-verbal manner.
Connection to Stress and Anxiety
The connection between emotional suppression and stress or anxiety is particularly noteworthy. When you suppress your emotions, you may inadvertently increase your stress levels as unresolved feelings accumulate over time. This buildup can lead to heightened anxiety as your mind grapples with unprocessed emotions.
You might notice that when you finally allow yourself to feel and express these emotions, there is often a sense of relief that follows. Understanding this connection can empower you to take proactive steps toward managing stress and anxiety more effectively. By recognizing when you are suppressing emotions, you can implement strategies to address those feelings head-on rather than allowing them to fester beneath the surface.
This shift in perspective can lead to healthier coping mechanisms and ultimately contribute to improved mental health.
Importance of Emotional Expression
Emotional expression plays a vital role in maintaining psychological well-being. You may find that allowing yourself to express emotions fosters deeper connections with others and enhances your overall quality of life. When you share your feelings with trusted friends or family members, it creates an opportunity for support and understanding, reinforcing social bonds that are essential for mental health.
Moreover, expressing emotions can serve as a form of catharsis, providing relief from pent-up feelings that may otherwise lead to distress. You might discover that simply talking about your experiences or sharing your thoughts with someone else can lighten the emotional load you carry. Recognizing the importance of emotional expression is a crucial step toward cultivating healthier relationships with yourself and others.
Applications in Therapy and Counseling
The insights gained from studies on emotional suppression have significant applications in therapy and counseling settings. Mental health professionals are increasingly recognizing the importance of addressing emotional expression as part of treatment plans. You may find that therapists incorporate techniques aimed at helping clients explore their feelings more openly, fostering an environment where emotional expression is encouraged rather than stifled.
Therapeutic approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) often emphasize identifying and challenging negative thought patterns related to emotional expression. By working with a therapist, you can develop healthier coping strategies that prioritize emotional awareness and expression over suppression. This shift can lead to improved mental health outcomes and a greater sense of empowerment in managing your emotions.
Conclusion and Future Research
In conclusion, the exploration of emotional suppression reveals its complex relationship with brain activity and mental health outcomes. As you reflect on the findings from recent studies, it becomes clear that addressing emotional expression is essential for fostering psychological well-being. The implications for mental health are profound, highlighting the need for individuals and professionals alike to prioritize healthy emotional management.
Future research in this area holds great promise for further understanding the nuances of emotional suppression and its effects on mental health. As scientists continue to investigate the neural mechanisms behind emotional regulation, there is potential for developing more effective therapeutic interventions aimed at promoting healthy emotional expression. By embracing this knowledge, you can take proactive steps toward nurturing your emotional well-being and fostering deeper connections with yourself and others.
Recent studies on brain scans have shed light on the mechanisms of emotional suppression, revealing how our brains respond when we try to hide our feelings.